CYANURIC CHLORIDE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
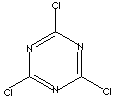
184.41
HS CODE
TOXICITY
Oral rat LD50: 930 mg/kg
Cyanurchlorid(German); Chlorure de cyanuryle(French); Cloruro di cianurile (Italian); 2,4,6-Trichloro-1,3,5-triazine; Tricyanogen chloride; sym-Trichlorotriazine; Kyanurchlorid (Czech); Cyanuryl chloride; Trichlorocyanidine; s-Triazine trichloride; 2,4,6-Trichloro-s-triazine; 1,3,5-Trichlorotriazine; Cyanur chloride; Cyanurchloride; Cyanuric acid chloride; Cyanuric acid trichloride; Cyanuric chloride; Cyanuric trichloride; Cyanuryl chloride; Tricholorotriazine; Tricyanogen chloride; Other RN: 190086-22-7
c1(nc(nc(n1)Cl)Cl)Cl
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
UN2670 [Corrosive]
Reagent for the conversion of alcohols
to chlorides, alcohols to iodides
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
clear crystals with pungent odor
1.32
Reacts
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Cyanuric chloride
PubChem Compound Summary - Cyanuric chloride
SIDS Initial Assessment Report - Cyanuric chloride
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ - Cyanuric chloride
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Cyanuric chloride
Local:
Triazine is the chemical species of six-membered heterocyclic ring compound with
three nitrogens replacing carbon-hydrogen units in the benzene ring structure.
The names of the three isomers indicate which of the carbon-hydrogen units on
the benzene ring position of the molecule have been replaced by nitrogens,
called 1,2,3-triazine, 1,2,4-triazine, and 1,3,5-triazine respectively.
Symmetrical 1,3,5-triazine is the common. Triazines are prepared from
2-azidocyclopropene through thermal rearrangement (1,2,3-triazine), from
1,2-dicarbonyl compound with amidrazone by condensation reaction
(1,2,4-triazine) and from cyanic acid amide by trimerization (1,3,5-triazine).
Pyridine is the aromatic nitrogen heterocycle compound having only one nitrogen,
and diazines are with 2 nitrogen atoms and tetrazines are with 4 nitrogen atoms
on the benzene ring system. Triazines are weak base. Triazines have much weaker
resonance energy than benzene, so nucleophilic substitution is preferred than
electrophilic substitution. Triazines are basic structure of herbicides,
examples are amitole (CAS #: 61-82-5), atrazine (CAS #: 1912-24-9), cyanazine
(CAS #: 21725-46-2), simazine (CAS #: 122-34-9), trietazine (CAS #: 1912-26-1).
Large volume of triazines are used in the manufacture of resin modifiers such
as melamine and benzoguanamine. Melamine (1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine) is
reacted with formaldehyde to from a very durable thermoset resin. Benzoguanamine
(2,4-Diamino-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine) is used to increase thermoset properties
of alkyd, acrylic and formaldehyde resins. Triazines are also useful as
chromophore groups in colorants and Chlorine attached in Triazine compounds
undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions well with with hydroxyl groups in
cellulose fibres. Some triazine family compounds are used in pharmaceutical
industry as coupling agent for the synthesis of peptide in solid phase as well
as solution and as side chain of antibiotics. Triazine compounds are used in
formulating bactericide and fungicide. They are used as preservatives in oil
field applications. They are used as disinfectant, industrial deodorant and
biocide in water treatment. They are used as a bleaching agents.
Cyanic acid (the isomer of fulminic acid) is an unstable (explosive), poisonous, volatile, clear liquid with the structure of H-O-C��N (the oxoacid formed from the pseudohalogen cyanide), which is readily converted to cyamelide and fulminic acid. There is another isomeric cyanic acid with the structure of H-N=C=O, called isocyanic acid. Cyanate group (and isocyanate group) can react with itself. Cyanuric acid (also called pyrolithic acid), white monoclinic crystal with the structure of [HOC(NCOH)2N], is the trimer of cyanic acid. The trimer of isocyanic acid is called biuret.
- Cyanic acid: H-N=C=O or H-O-C��N
- Fulminic acid: (H-C=N-O) or H-C��N-O
- Isocyanic acid: H-N=C=O
- Cyanuric acid: HOC(NCOH)2N
- Biuret: (NH2)CO)2 NH
Cyanic acid hydrolyses to ammonia and carbon dioxide in water. The salts and esters of cyanic acid are cyanates. But esters of normal cyanic acid are not known. The salts and esters of isocyanic acid are isocyanates. The isocyanate group reacts with the hydroxyl functional group to form a urethane linkage. Diisocyanates (or polyisocyanates) are monomers for polyurethane production. Polyurethane is made from a variety of diisocyanates in conjunction with polyether and polyester polyols as co-reactants by addition polymerization which needs at least two -N=C=O groups. Polyurethanes are widely used in the manufacture of flexible and rigid foams, fibres, coatings, and elastomers. If isocyanate monomer is polymerized with amine group, polyurea is produced. Cyanates (or Isocyanates) are readily reacts with various form of amine (including ammonia, primary-, secondary-amines, amides and ureas) and hydroxyl functional group. They are used in the synthesis for the target molecules such as pharmaceuticals, pesticides, textile softener, lubricants and industrial disinfectants. They can convert to polycyclic compounds such as hydantoins and imidazolons. They are used as plastic additives and as heat treatment salt formulations for metals.
An amino compound with azo, phthalocyanine, or anthraquinone group is condensed in an aqueous medium with cyanuric chloride. Cyanuric chloride is used as an intermediate for manufacturing agrochemicals,dyestuffs, optical brighteners, tanning agents, softening agents and pharmaceuticals. Building block for plastics and additives. Cyanuric chloride is used as a catalyst in the The Beckmann reaction, rearrangement reaction of an oxime to an amide (corresponding lactam used for the production of nylon fibers)
APPEARANCE
white crystalline powder
ASSAY
99.0% min
INSOLUBLES
0.5% max (in Toluene and Acetonitrile)
MELTING POINT
145 C min
SIEVE ANALYSIS
Fitness (160 ��m) remaining 5%
8 (Packing group : II)
2670
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Highly toxic by inhalation, Toxic by ingestion, Skin sensitiser, Corrosive. Target Organs: Central nervous system, Heart
GHS
PICTOGRAMS


HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302-H314-H317-H330
P STATEMENTS
P260-P280-P284-P305 + P351 + P338-P310
![]()
![]()
RISK PHRASES
14-22-26-34-43
SAFETY PHRASES
26-28-36/37/39-45-46-63